Exploring Cardano: A New Era in Smart Contract Technology
Written on
Introduction to Cardano
Cardano emerged as a significant player in the blockchain space when it launched in 2017, gaining recognition amidst a surge of ICO-driven projects. Unlike many of its counterparts that succumbed to market pressures, Cardano has shown resilience, especially following the Shelley hard fork in July 2020. This marked a revival for the platform, propelling it into the top ranks of cryptocurrency by market capitalization throughout 2021. In a field crowded with Layer-1 smart contract platforms, Cardano's distinct philosophy and approach could provide it with a competitive advantage, assuming its ongoing developments yield positive outcomes.
The project is deeply rooted in values such as community governance, academic rigor, and high assurance programming, which have significantly influenced its design and development trajectory. This commitment to establishing a decentralized global financial infrastructure rather than merely focusing on Web3 experiences may explain its recent popularity, highlighted by a poll from Ethereum's co-founder, Vitalik Buterin, regarding preferred currencies for the global financial system by 2035. Cardano's unique design and values have also facilitated key governmental partnerships and a strategic alliance with DISH Network.
However, the project’s meticulous design choices have sometimes led to prolonged development timelines, posing a challenge to its adoption in a fast-evolving Web3 landscape where users often prioritize immediate financial opportunities over idealistic values of decentralization and security. Despite these challenges, Cardano boasts a robust community, as evidenced by various on-chain and off-chain metrics, and the rollout of decentralized applications (dApps) signals that the platform is only at the beginning of its journey.
Understanding Cardano
Cardano is an open-source, permissionless blockchain network utilizing a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, built upon the foundation of over 120 scholarly articles. The core of the project is its base layer blockchain, which aspires to create a sustainable, community-governed ecosystem underpinned by a trustless settlement layer for peer-to-peer transactions and digital agreements. The project aims to empower approximately 2 to 3 billion individuals globally who lack digital and financial identities, with a particular focus on initiatives in Africa. IOG, Cardano’s lead development organization, is already collaborating with governmental bodies in three countries.
The ambitious goals of Cardano necessitate that its infrastructure operates flawlessly from the outset, contrasting sharply with the "launch now, fix later" mentality prevalent among many Silicon Valley teams. This has led to a culture emphasizing academic peer review and formal verification, prioritizing security and reliability, albeit at the cost of slower development.
Founders and Structure
Founded in 2015 by Charles Hoskinson and Jeremy Wood—co-founders of Ethereum—Cardano's development is driven by three organizations, each with distinct roles:
- Input Output Global (IOG or IOHK): A for-profit blockchain research and engineering firm leading the development of Cardano.
- EMURGO: A for-profit entity focused on promoting Cardano-based commercial applications.
- Cardano Foundation: An independent non-profit organization based in Switzerland, responsible for overseeing the development and governance of the Cardano blockchain.
This separation of responsibilities is a common practice in many blockchain initiatives, designed to keep business interests distinct from the development of community-centric, public infrastructure. Notably, the independence of the Cardano Foundation from the original development team highlights the project’s commitment to community governance.
Third-Generation Blockchain Characteristics
Cardano is classified as a third-generation blockchain, designed to enhance smart contract functionality while emphasizing scalability, interoperability, and sustainability. It seeks to overcome the limitations of first-generation (Bitcoin) and second-generation (Ethereum) blockchains:
- Scalability: The capability to accommodate a growing user base, targeting billions of users.
- Interoperability: The ability to interact seamlessly with other blockchains and external resources.
- Sustainability: Ensures low energy consumption and employs community governance for long-term ecosystem viability.
Competing projects like Ethereum 2.0, Polkadot, and Solana are often seen as rivals to Ethereum, yet they aim to coexist in a decentralized Web3 ecosystem. Interestingly, while often labeled as “Ethereum killers,” Cardano shares more similarities with Bitcoin regarding its tokenomics, consensus protocol, and accounting methods.
Tokenomics and Initial Distribution
Cardano's cryptocurrency, ADA, mirrors Bitcoin’s tokenomics, featuring a capped supply of 45 billion coins. The initial distribution occurred through a five-round ICO from September 2015 to February 2017, raising a total of $79.2 million and allocating a significant portion to the founding organizations while maintaining a sizable reserve for future distribution.
The project’s decision to distribute 83% of the initial circulating supply to the public stands out compared to its peers, which often reserve a large percentage for insiders. This commitment to equitable distribution is vital in promoting broader community engagement and governance.
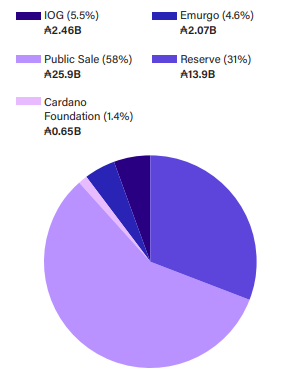
Current ADA Supply Distribution
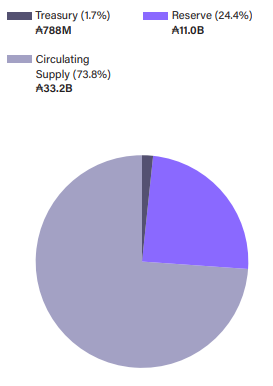
Monetary Expansion and Treasury Management
Despite launching in September 2017, staking rewards only began distribution after the Shelley hard fork in July 2020. This monetary expansion targets a depletion rate of 0.3% per epoch, leading to a reserve half-life of approximately 4 to 5 years. The distribution model allocates 80% of rewards to stake pools and delegators, while 20% supports community-driven projects through the treasury.
Roadmap to Decentralization
Cardano's development roadmap is divided into five key phases, each focusing on milestones that promote community governance and sustainability:
- Byron: The initial launch of the base layer in September 2017 as a federated network.
- Shelley: Decentralization efforts transitioned the network to community-operated nodes.
- Goguen: The introduction of multi-asset support and smart contracts.
- Basho: Enhancements in scalability and interoperability.
- Voltaire: Governance features for long-term sustainability.
Technological Innovations
Most Layer-1 smart contract platforms share similarities, but their technical underpinnings differentiate them. Cardano's design is particularly unique, resembling a PoS-enabled version of Bitcoin due to its protocol and accounting model. Key features include:
- Ouroboros Protocol: The consensus mechanism that combines PoS with Nakamoto-style consensus.
- EUTxO Model: An extension of Bitcoin’s UTxO model that integrates smart contract capabilities.
- Haskell Programming: A functional programming language that enhances reliability and security.
Ouroboros and Its Upgrades
Ouroboros stands at the core of Cardano's blockchain, utilizing a consensus protocol that allows nodes to agree on transaction validity. This approach enhances energy efficiency compared to PoW systems and addresses ethical concerns associated with PoS protocols.
The protocol's unique design fosters improved throughput and security, with initial tests showing a capacity of up to 257 transactions per second.
Staking and Stake Distribution
Cardano's staking system allows validators to earn rewards while promoting an egalitarian participation model through stake delegation. This ensures that ADA holders can still participate in network security while delegating their tokens.
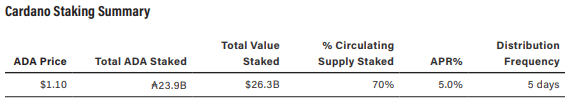
The distribution of stake across the network is crucial for decentralization, with over 23.9 billion ADA staked among 3,100 stake pools. Notably, Cardano's decentralization metrics outshine those of Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Liquid Democracy and Delegation Experience
Cardano’s delegation mechanism embodies a liquid democracy, allowing ADA holders to unstake their tokens without penalties or unbonding periods. This design promotes higher participation rates, as users retain liquidity for trading and other activities.
No Slashing Policy
Unlike other PoS protocols, Cardano does not impose slashing penalties, alleviating risks for delegators and potentially enhancing participation rates.
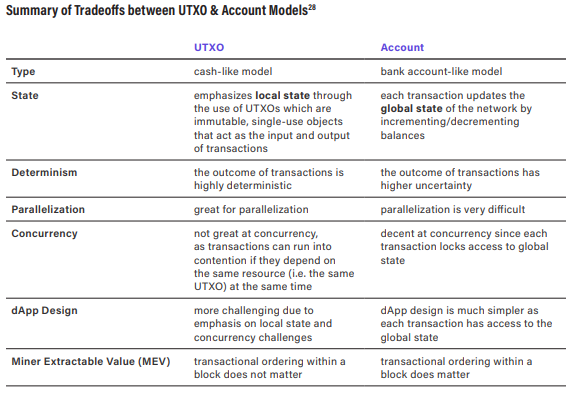
Extended UTXO Model
The Extended UTXO (EUTxO) model allows for the incorporation of metadata and scripts, facilitating smart contracts while maintaining the benefits of the UTXO model. This structure enhances efficiency and security for transactions.
Catalyst and Community Governance
Project Catalyst serves as Cardano's governance framework, enabling community members to propose initiatives for ecosystem development. Stakeholders can vote on proposals through a dedicated mobile app, ensuring that governance reflects community interests.
Web3 Ecosystem Development
Cardano's Web3 ecosystem is gradually taking shape, with numerous projects in various stages of development. While the initial rollout of dApps has been slower than anticipated, the network has seen significant activity, including the launch of its first decentralized exchanges.
Initial Stake Pool Offerings
A notable innovation within Cardano is the Initial Stake Pool Offering (ISPO), which allows projects to distribute tokens to delegators in exchange for staking rewards. This mechanism has sparked interest and debate within the community.
Network Growth and Institutional Interest
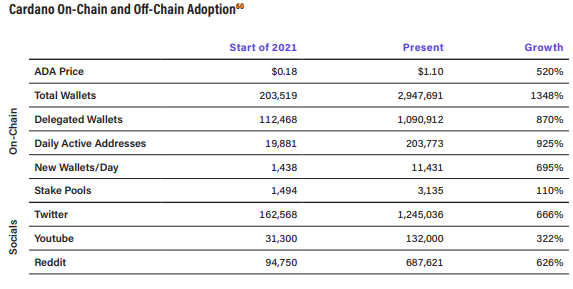
Cardano experienced remarkable growth in adoption metrics throughout 2021, propelled by major upgrades and increasing interest across the crypto landscape. The network has seen significant wallet growth and transaction activity.
Major Partnerships
Cardano has established significant partnerships with governmental and commercial entities, including projects aimed at improving educational systems and providing decentralized identity solutions.
Conclusion
In summary, Cardano represents a multi-dimensional initiative with a compelling vision. Its unique combination of innovative features, robust academic foundations, and community-oriented approach positions it as a key player in the competitive landscape of Layer-1 smart contract platforms. Looking ahead, the ongoing rollout of dApps and enhancements in network performance may pave the way for Cardano to achieve its ambitious goals in the blockchain space.