The Promise of Hydrogen: Navigating Towards a Sustainable Future
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Hydrogen's Role in Climate Solutions
Hydrogen, recognized as the universe's most abundant element, is often celebrated as a potential solution to combat climate change. It has the capability to replace fossil fuels and provide a sustainable energy alternative in various sectors, including transportation, heavy industry, and power generation. However, the effectiveness of hydrogen as a green energy source is contingent on its production methods.
The role of hydrogen in addressing climate change is significant, as it can help reduce carbon emissions, facilitate the decarbonization of transportation and industrial processes, and enable energy storage. The crux lies in ensuring that hydrogen is produced sustainably, with a preference for renewable energy sources.
Hydrogen can be derived from multiple sources, including renewable options like solar and wind energy, as well as non-renewable sources, such as natural gas, via steam methane reforming. When utilized, hydrogen's only byproduct is water, making it a remarkably clean fuel. Thus, it is crucial to focus on sustainable production methods for hydrogen.
The concept of the "hydrogen rainbow" is pivotal here. This term refers to the various colors associated with different hydrogen production processes, serving as a shorthand to convey the method and its environmental impact. Although hydrogen itself is colorless, the production method significantly influences its environmental footprint, and the hydrogen rainbow categorizes these methods accordingly.
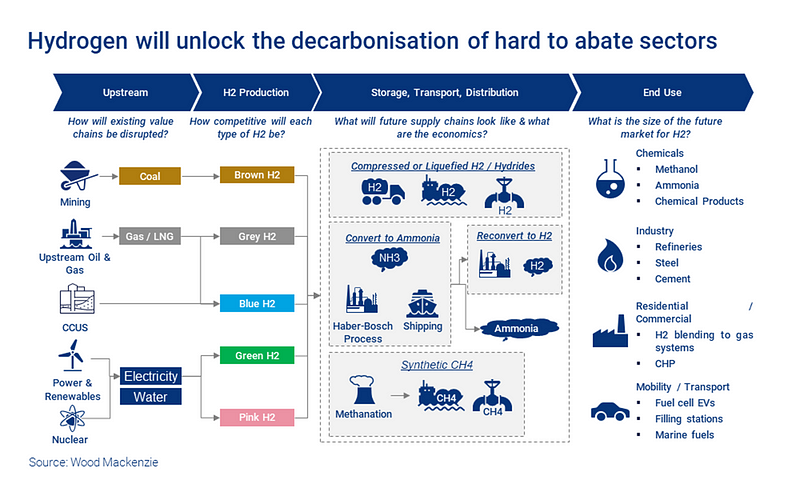
Chapter 2: The Spectrum of Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen is predominantly produced through steam methane reforming (SMR), which reacts natural gas with steam to yield hydrogen and carbon dioxide. This method is often labeled "Grey hydrogen" due to its substantial carbon emissions. The challenge with grey hydrogen lies in its non-carbon-neutral nature, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbates climate change. The International Energy Agency noted that grey hydrogen constituted around 80% of hydrogen production in 2020, making it a major source of global carbon emissions.
Nevertheless, a cleaner production method exists. "Green hydrogen" is generated using renewable energy sources like wind, solar, or hydropower, which do not emit greenhouse gases. This is achieved through electrolysis, where an electric current divides water into hydrogen and oxygen. Although green hydrogen production is currently more costly than its grey counterpart, prices are anticipated to decrease as renewable energy becomes more economical.
The video from MIT Technology Review discusses the future of technology and emphasizes the importance of green solutions like hydrogen in addressing upcoming energy challenges.
"Blue hydrogen" is produced similarly to grey hydrogen but incorporates carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology, which traps carbon dioxide emissions before they enter the atmosphere. While blue hydrogen still relies on fossil fuels, it has a significantly reduced carbon footprint compared to grey hydrogen and is viewed as a transitional solution toward renewable energy.
Another emerging category, "Pink hydrogen," utilizes renewable energy to produce hydrogen from waste biomass through gasification, a method that converts organic waste into hydrogen-rich gas. While still experimental, pink hydrogen holds promise for sustainable production.
"Brown and Black hydrogen," derived from coal, represent significant carbon emissions, and both terms are often used interchangeably due to their similar emissions profiles. Conversely, "Turquoise hydrogen" is a novel approach created through methane pyrolysis, which generates solid carbon rather than requiring CCS for carbon capture; this solid carbon can be repurposed for products like fertilizers.
As of 2021, hydrogen demand reached 94 million metric tons, primarily driven by oil refining and the production of ammonia for fertilizers and methanol for chemical manufacturing.
Chapter 3: Future Prospects and Investments in Hydrogen
Looking ahead, hydrogen utilization is expected to expand as it offers a viable alternative to fossil fuels in transportation, heavy industry, and other sectors. If nations meet their climate goals, hydrogen demand could soar to 130 million metric tons by 2030, with about 25% attributed to innovative applications.
Governments globally are acknowledging the potential of green hydrogen and are investing in its development. For instance, the European Commission has recently established regulations defining "renewable" hydrogen, a move aimed at guiding the growth of the green hydrogen sector. Similarly, in the US, the Biden administration is formulating tax credit policies to support hydrogen production.
Hydrogen stands to be a transformative element in the fight against climate change, provided it is produced through clean energy methods. Green hydrogen is key to unlocking its advantages as a sustainable energy source. Continued investment and technological advancements in green hydrogen are essential to making it more affordable and accessible. By prioritizing these developments, hydrogen can play a significant role in fostering a cleaner, more sustainable future.